Key Highlights
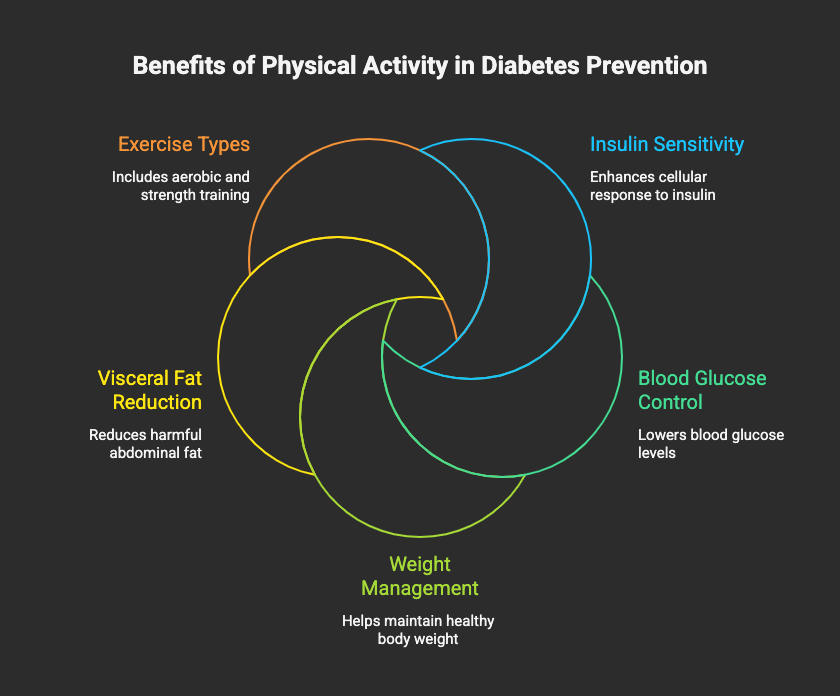
- Regular physical activity is a powerful tool for preventing type 2 diabetes by improving how your body uses insulin.
- Exercise helps lower blood glucose by prompting muscles to absorb sugar from the bloodstream.
- Both aerobic exercise and strength training are crucial, with a combination offering the most significant benefits for diabetes risk reduction.
- Physical activity helps you manage your body weight and reduce harmful visceral fat, a key factor in insulin resistance.
- Consistent exercise improves insulin sensitivity, making your cells more responsive to insulin.
Introduction
Are you looking for a proactive way to protect your health and reduce your risk of chronic disease? If you’re working to prevent type 2 diabetes, incorporating regular physical activity into your routine is one of the most effective steps you can take. Exercise isn’t just about weight management; it directly impacts your body’s ability to control blood sugar and use insulin effectively. This guide will explore how movement serves as a cornerstone of diabetes prevention for adults.
Understanding Type 2 Diabetes in Adults
Type 2 diabetes is a chronic metabolic condition characterized by high levels of blood glucose. This occurs when your body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t effectively use the insulin it makes. This condition affects millions and is often linked to various risk factors, including lifestyle and genetics.
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes and its precursor, prediabetes, is a significant public health concern. According to the Diabetes Association, understanding this condition is the first step toward prevention. Let’s look closer at its characteristics, causes, and impact.
Causes and Risk Factors
Type 2 diabetes develops from a combination of genetic and lifestyle-related risk factors. While you can’t change your genetic predisposition, many other contributing factors are within your control. A primary cause is the development of insulin resistance, where your body’s cells become less sensitive to the effects of insulin.
Excess weight, particularly abdominal or visceral fat, is a major player. These fat cells are metabolically active and can release hormones and other substances that interfere with insulin action, putting you at high risk.
Other key risk factors include:
- A sedentary lifestyle with little to no regular exercise.
- An unhealthy diet.
- A family history of the disease.
Understanding and addressing these factors are essential for preventing the onset of type 2 diabetes.
Prevalence and Impact in the United States
The prevalence of type 2 diabetes and prediabetes in the United States is staggering. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) notes that more than one in three American adults have prediabetes, placing them at high risk of developing full-blown diabetes. This highlights a critical window of opportunity for prevention through lifestyle changes.
The impact of this condition extends far beyond blood sugar control. According to the American Diabetes Association, individuals with type 2 diabetes have a significantly higher risk of developing other serious health problems. The chronic inflammation and metabolic disruption associated with diabetes can damage organs and systems throughout the body.
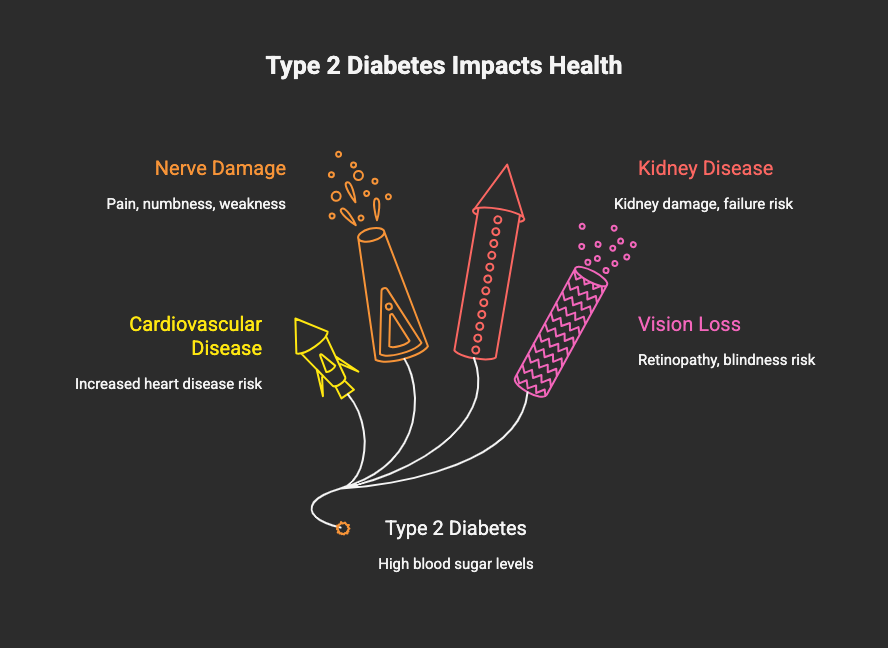
This leads to a higher incidence of severe complications.
|
Complication |
Impact on Health |
|---|---|
|
Cardiovascular Disease |
Increased risk of heart attack, stroke, and coronary artery disease. |
|
Nerve Damage (Neuropathy) |
Can cause pain, numbness, and weakness, especially in the extremities. |
|
Kidney Disease |
Prolonged high blood sugar can damage the kidneys, potentially leading to failure. |
|
Vision Loss |
Diabetes can lead to retinopathy, which may result in blindness. |
The Connection Between Physical Activity and Diabetes Prevention
Now that we understand type 2 diabetes, how can physical activity help? The link between regular movement and diabetes prevention is incredibly strong and supported by extensive research. Exercise directly tackles the core issues of the condition by helping to lower blood sugar and improve insulin sensitivity.
Engaging in physical activity is a proactive strategy to reduce your risk of not only diabetes but also related conditions like heart disease. The benefits begin with the very first session and accumulate over time, making it a vital component of a healthy lifestyle. The following sections will explain exactly how exercise achieves these protective effects.
Recommended Physical Activity Levels to Reduce Diabetes Risk
To get the most out of your efforts, it’s helpful to know how much exercise is recommended. Major health organizations have established clear physical activity guidelines based on extensive research. These recommendations provide a target for how much you should move each week to significantly reduce your diabetes risk.
Following these guidelines can help you structure your routine and ensure you’re getting the right amount and type of activity. Let’s break down what organizations like the American Diabetes Association suggest for frequency, intensity, and duration.
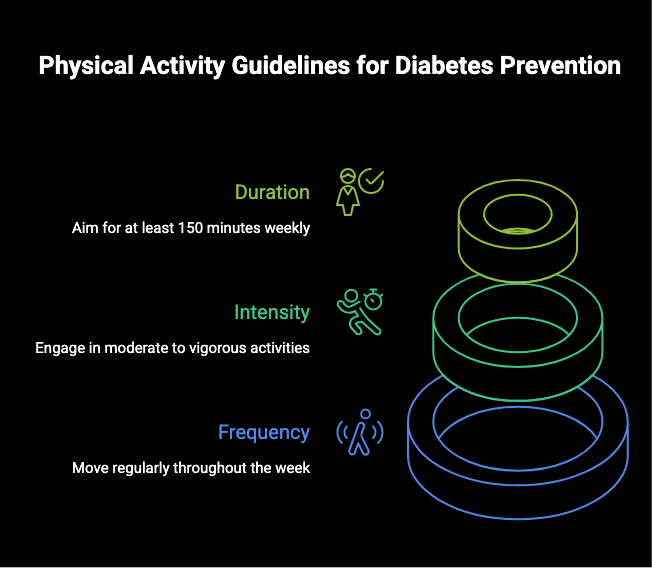
Guidelines from Major Health Organizations
The consensus among major health organizations like the American Diabetes Association (ADA) and the American Heart Association is clear. For substantial health benefits and diabetes prevention, adults should aim for a specific amount of activity each week. These physical activity guidelines are designed to be achievable and effective.
The recommendations emphasize consistency and a combination of different types of exercise. Spreading your workouts throughout the week is crucial to maintain improved insulin sensitivity. The guidelines also highlight the importance of not letting more than two days pass without some form of activity.
Here is a summary of the weekly guidelines from the American Diabetes Association:
|
Activity Type |
Recommendation |
|---|---|
|
Aerobic Activity |
At least 150 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise OR 75 minutes of vigorous-intensity exercise. |
|
Frequency |
Spread over at least 3 days per week. |
|
Resistance Training |
At least 2-3 sessions per week on nonconsecutive days. |
The Role of Diet in Diabetes Prevention
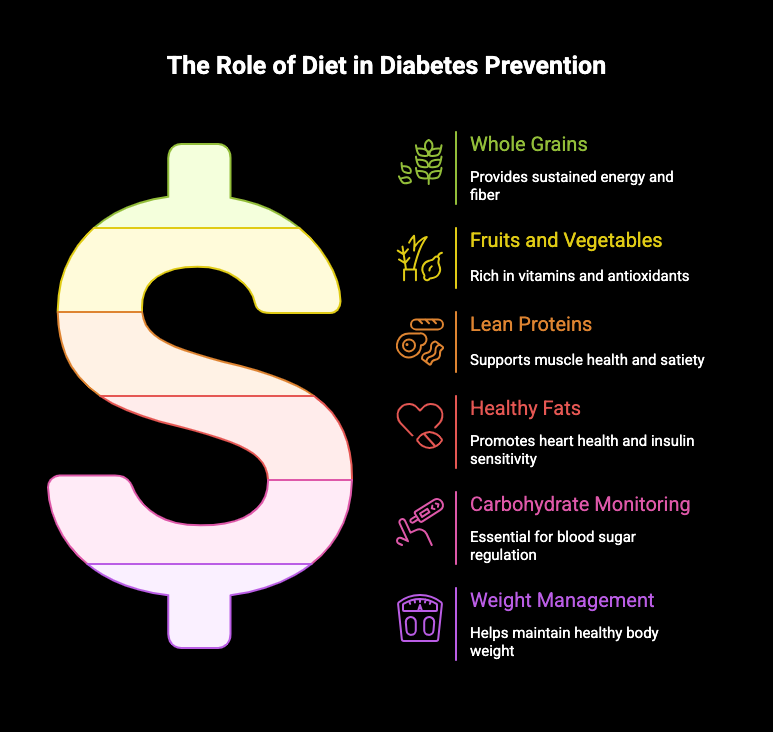
Good nutrition plays a vital role in diabetes prevention alongside physical activity. A balanced diet rich in whole grains, fruits, vegetables, and lean proteins can help regulate blood sugar levels and improve insulin sensitivity. Monitoring carbohydrate intake is essential, as it directly affects blood glucose. Healthy fats from sources like avocados and nuts can also support heart health, reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease linked to diabetes. By prioritizing nutritious foods and maintaining a healthy weight, individuals can decrease their diabetes risk and enhance overall wellness. Making mindful dietary choices is key to effective diabetes management.
Community Resources and Support Options
Connecting with community resources can significantly enhance your journey toward diabetes prevention and management. Local health organizations often provide classes focused on physical activity, nutrition, and overall wellness. Additionally, group exercise programs or clubs not only offer structured workouts but also foster social interactions that can motivate consistent participation. Support options, such as diabetes education programs and online forums, create a network for sharing experiences and tips. Utilizing these resources can help you stay committed, find new fitness routines, and better educate yourself about your health, ultimately contributing to improved blood glucose levels and enhanced overall well-being.
When to Seek Medical Advice
Knowing when to seek medical advice is crucial for anyone starting or adjusting an exercise program, especially those at risk of type two diabetes. Symptoms like unusual fatigue, significant changes in blood sugar levels, or signs of injury shouldn’t be ignored. Regular check-ins with healthcare providers can also help assess insulin sensitivity and monitor overall health. If you have chronic conditions or are over 65, consider discussing your exercise plans with a medical professional to ensure safety and effectiveness. Taking proactive steps can greatly affect diabetes management and overall well-being.
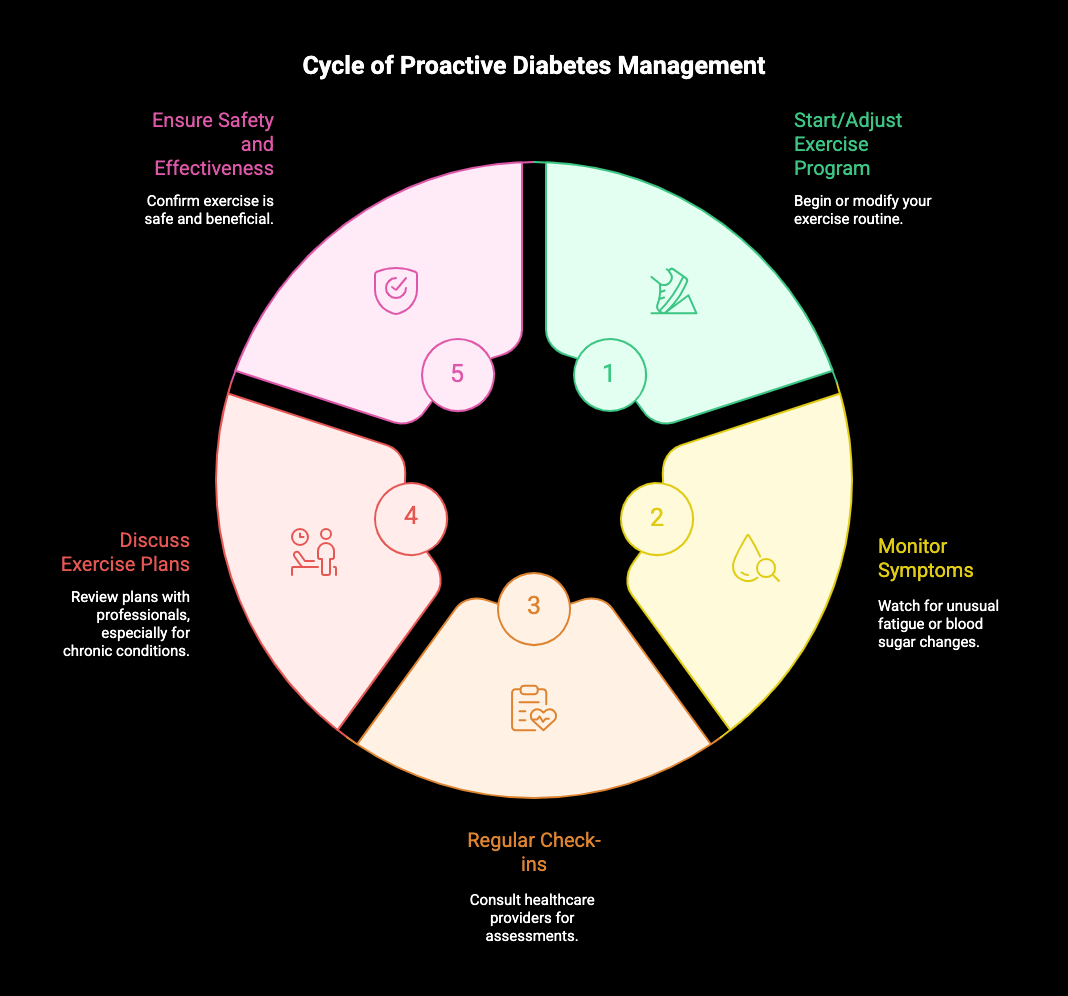
Regular physical activity plays a crucial role in preventing type two diabetes among older adults by improving insulin sensitivity and helping to maintain a healthy weight, ultimately reducing the risk of developing this chronic condition
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0167527313009212
https://www.thelancet.com/journals/lanpub/article/PIIS2468-2667(21)00302-9/fulltext
Conclusion
Adopting a regular routine of physical activity can play a crucial role in preventing type two diabetes. Engaging in activities like brisk walking, resistance training, or aerobic exercises not only helps maintain a healthy weight but also enhances insulin sensitivity and lowers blood sugar levels. Understanding how various forms of exercise impact the body is key to tailoring an effective approach. With consistent effort and the right resources, overcoming barriers to regular exercise is achievable. Embracing an active lifestyle fosters not just better glycemic control but also contributes to overall well-being, making daily life more enjoyable.
Frequently Asked Questions
How quickly can physical activity reduce my risk of type 2 diabetes?
Regular physical activity can significantly lower your risk of developing type 2 diabetes within a few weeks. Engaging in consistent exercise improves insulin sensitivity and helps maintain healthy weight, making it an effective preventive measure against diabetes for adults.
Are certain exercises more effective than others for preventing diabetes?
Certain exercises, like aerobic activities and strength training, enhance insulin sensitivity and glucose metabolism, making them particularly effective in diabetes prevention. Engaging in a mix of high-intensity interval training (HIIT) and moderate exercises can yield optimal benefits for maintaining healthy blood sugar levels.
Is it safe to start exercising if I have risk factors for diabetes?
If you have risk factors for diabetes, starting an exercise routine can be safe and beneficial. However, it’s crucial to consult with a healthcare professional first. They can assess your individual circumstances and provide personalized recommendations to ensure a safe approach to physical activity.