Key Highlights
Here are the main takeaways from this guide:
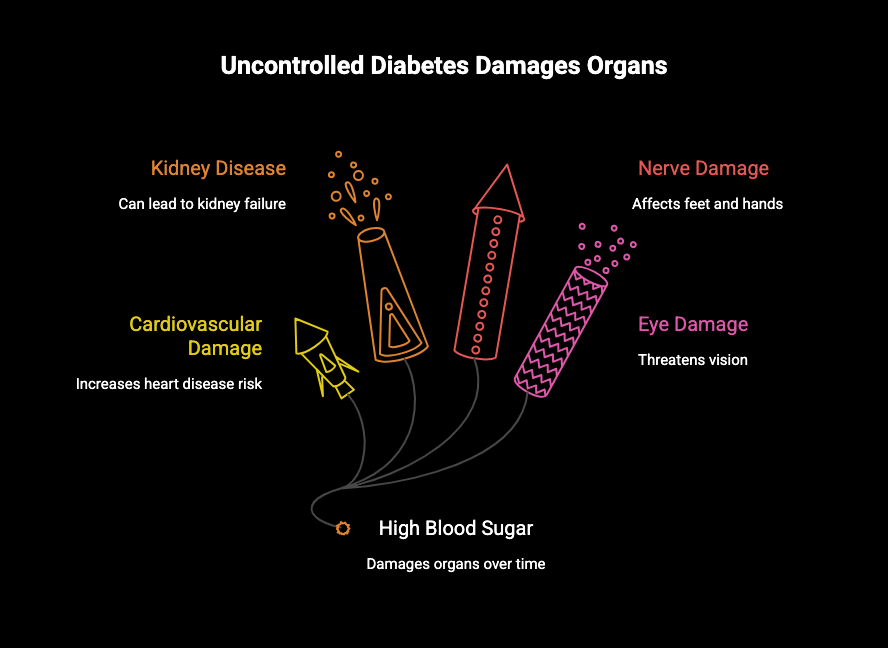
- Uncontrolled diabetes can lead to high blood sugar, which damages organs over time.
- The cardiovascular system is at high risk, increasing the chances of heart disease and stroke due to damaged blood vessels.
- Diabetes is a leading cause of kidney disease, potentially leading to kidney failure if not managed.
- Nerve damage, or diabetic neuropathy, is a common complication, often affecting the feet and hands first.
- Eye health is a major concern, with conditions like diabetic retinopathy posing a threat to your vision.
- Managing blood sugar through a healthy lifestyle and treatment is the best way to protect your organs.
Introduction
Living with diabetes mellitus means being mindful of how it affects your entire body. While many people focus on daily blood sugar management, it’s crucial to understand the long-term impact on your organs, including your oral health and the potential for gum disease. High glucose levels can quietly cause damage over time, increasing the risk of serious health problems. The good news is that with early diagnosis and a solid treatment plan, you can significantly reduce the risk of diabetes complications and protect your health for years to come.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Impact on the Body
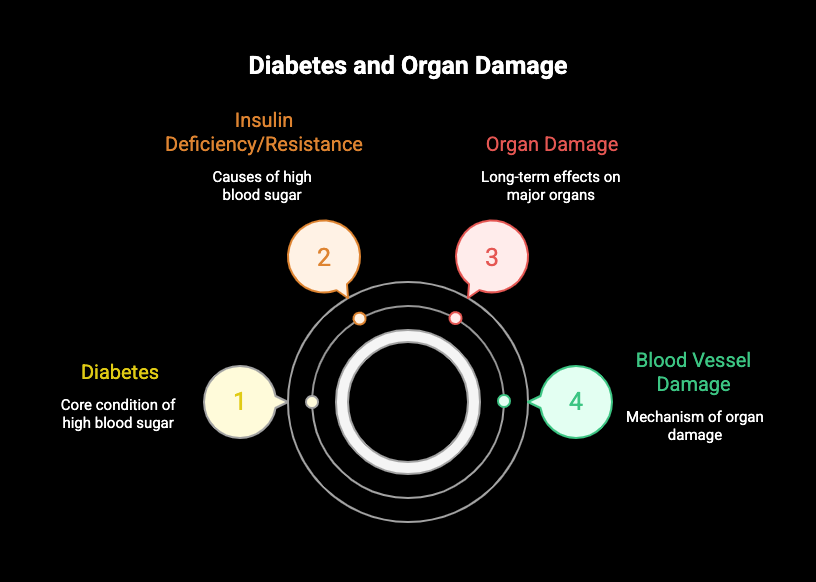
Diabetes is a condition where your blood glucose, or blood sugar, is too high. This happens because your body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t use it effectively, often due to insulin resistance. There are different types of diabetes, but they all share a common problem: high blood sugar that, if unmanaged, can harm your body.
Over time, elevated glucose can damage major organs like your heart, kidneys, and eyes by harming the blood vessels that supply them with oxygen and nutrients. Let’s explore what happens when blood sugar isn’t controlled and how different types of diabetes, including gestational diabetes, can impact your organs.
Diabetes and Hypertension
Diabetes, high cholesterol, and high blood pressure, or hypertension, often go hand in hand. Nearly 74% of adults with diabetes also have high blood pressure, creating a dangerous combination that dramatically increases the risk of cardiovascular disease. The two conditions share many of the same risk factors, including obesity and an unhealthy diet.
Preventing Cardiovascular Complications
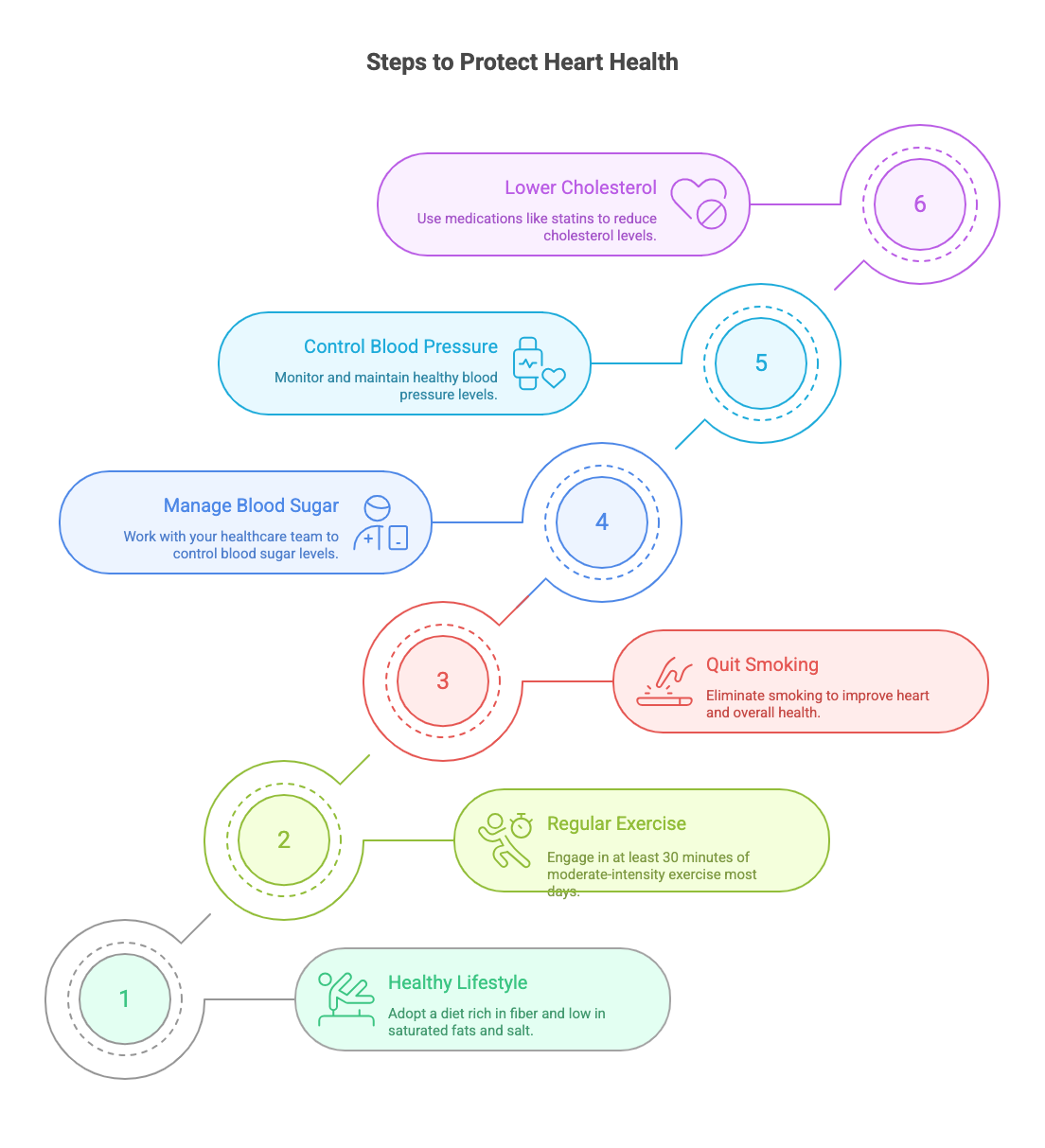
The good news is that you can take proactive steps to protect your heart and prevent cardiovascular complications, including blood vessel damage. The key is a combination of lifestyle changes and sticking to your treatment plan. Adopting a healthy lifestyle is one of the most powerful tools you have.
Working with your healthcare team to manage your blood sugar, blood pressure, and cholesterol levels is essential for all parts of your body. Your doctor might prescribe medications like statins to lower cholesterol or other drugs to help protect your heart. Small, consistent efforts can lead to significant long-term benefits for your cardiovascular health.
Here are some effective strategies to get started:
- Maintain a healthy diet rich in fiber and low in saturated fats and salt.
- Engage in regular physical activity, aiming for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days.
- If you smoke, quitting is one of the best things you can do for your heart and overall health.
The Kidneys and Diabetes: Risks and Changes
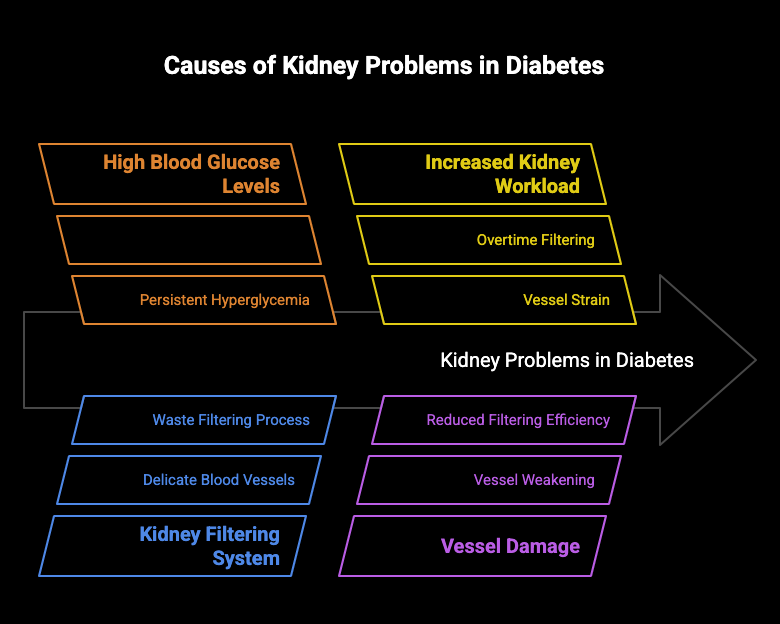
Your kidneys work as sophisticated filters, but high blood glucose can damage them over time. Weight loss is important as diabetes is one of the leading causes of kidney disease, affecting about one in three adults with the condition. When the small blood vessels in your kidneys are damaged, they can’t filter waste from your blood effectively.
Why Kidney Problems Occur in Diabetes
Kidney problems develop in people with diabetes because persistently high blood glucose levels damage the delicate filtering system of the kidneys, impacting overall kidney function. Your kidneys contain millions of tiny blood vessel clusters that filter waste from your blood. High blood sugar forces the kidneys to work harder and, over time, damages these vessels.
Eye Health and Vision Concerns in Diabetes
Your eye health is another area where diabetes can have a profound impact on the immune system. High blood sugar can damage the tiny blood vessels in the retina, the light-sensitive tissue at the back of your eye. This can lead to serious vision issues, including a condition called diabetic retinopathy, which is a leading cause of blindness in adults.
Retinopathy and Other Vision Issues
Diabetic retinopathy is the most common eye complication for people with diabetes. It occurs when high blood glucose damages the blood vessels in the retina, contributing to blood vessel disease. In the early stages, these vessels may leak fluid or blood. As the condition progresses, your body may try to grow new, weaker blood vessels that are prone to bleeding, which can obscure your vision.
Feet Health and Related Complications
Your feet are particularly vulnerable to complications from diabetes due to the combined effects of poor blood flow and nerve damage, which can also be linked to chronic kidney disease. High glucose levels can make you lose sensation in your feet, meaning you might not feel a small cut, blister, or sore. This lack of feeling can be very dangerous.
When a foot injury goes unnoticed, it can quickly become infected. Poor circulation slows down the healing process, allowing bacterial infections to worsen. A simple blister can turn into a serious foot ulcer that is difficult to treat. In the most severe cases, this can lead to tissue death and may require amputation. In the United States, a loss of consciousness is not directly related to foot health but is a severe symptom of dangerously high or low blood sugar.
Diabetes Effects on Sexual Health and Fertility
Diabetes can have a significant impact on sexual function and fertility in both men and women. The damage to blood vessels and nerves caused by high blood sugar can interfere with sexual response. In men, reduced blood flow to the penis can lead to erectile dysfunction, which is more than three times more likely in men with diabetes. Common signs that diabetes is impacting internal organs include persistent fatigue, numbness or tingling in the extremities, vision changes, slow-healing wounds, and kidney-related issues such as swelling in the legs or changes in urine output. In severe cases, these kidney-related issues may necessitate a kidney transplant. These symptoms may indicate that diabetes is affecting blood vessels and nerves throughout the body, not just those related to sexual health.
Conclusion
In conclusion, understanding how diabetes affects your organs is crucial for managing the disease effectively. From cardiovascular complications, including heart attacks, to nerve damage, diabetes can have widespread implications on your body. Early detection and proactive strategies are key to preserving your health and preventing serious complications. By adopting a healthy lifestyle, staying informed about the risks, and regularly consulting with healthcare professionals, you can significantly improve your quality of life. Remember, taking charge of your health is empowering, so make it a priority today. If you want personalized advice on managing diabetes and protecting your organs, reach out for a free consultation with our experts!
Frequently Asked Questions
Which organs are affected first by diabetes?
The first organs affected by diabetes are often those with a rich supply of small blood vessels. High levels of blood sugar tend to damage the delicate vessels in the kidneys and eyes first, increasing the risk of kidney disease and impacting eye health. The nerves, particularly in the feet and hands, are also highly susceptible to early damage.
Can diabetes cause permanent organ damage and how can this be prevented?
Yes, diabetes can cause permanent organ damage, including nerve damage, kidney damage, heart disease, and various skin conditions. The best way to prevent this is by managing your blood glucose levels through consistent lifestyle changes, medication as prescribed, and regular medical check-ups. Early and proactive management is key to protecting your organs.
How does managing diabetes help protect internal organs?
Managing diabetes, regardless of the type of diabetes, protects your organs by keeping blood sugar levels in a healthy range, which prevents damage to blood vessels and nerves. Following your treatment plan, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and working with your healthcare provider also helps control related risks like high blood pressure, further safeguarding your organs.


