Key Highlights
Introduction
Exploring the journey of diabetes management reveals a landscape filled with hope and potential. Many are on a quest for better understanding and, ultimately, the possibility of reversing their condition. By examining the intricacies of blood sugar levels, insulin sensitivity, and lifestyle changes, we can unveil the evolving perspective on diabetes. This blog aims to shed light on recent research and practical strategies that support the quest for diabetes remission, allowing individuals to improve their quality of life.
Understanding Diabetes and Its Types
Diabetes is a chronic disease that affects how the body processes blood sugar levels. There are primarily three types: Type 1, Type 2, and Prediabetes. Type 1 diabetes occurs when the body doesn’t produce enough insulin due to the destruction of beta cells. Type 2 diabetes, more prevalent, is often linked to insulin resistance and can be influenced by lifestyle changes, including diet and exercise. Prediabetes indicates elevated blood glucose levels, but it’s possible to reverse this condition with proactive measures.
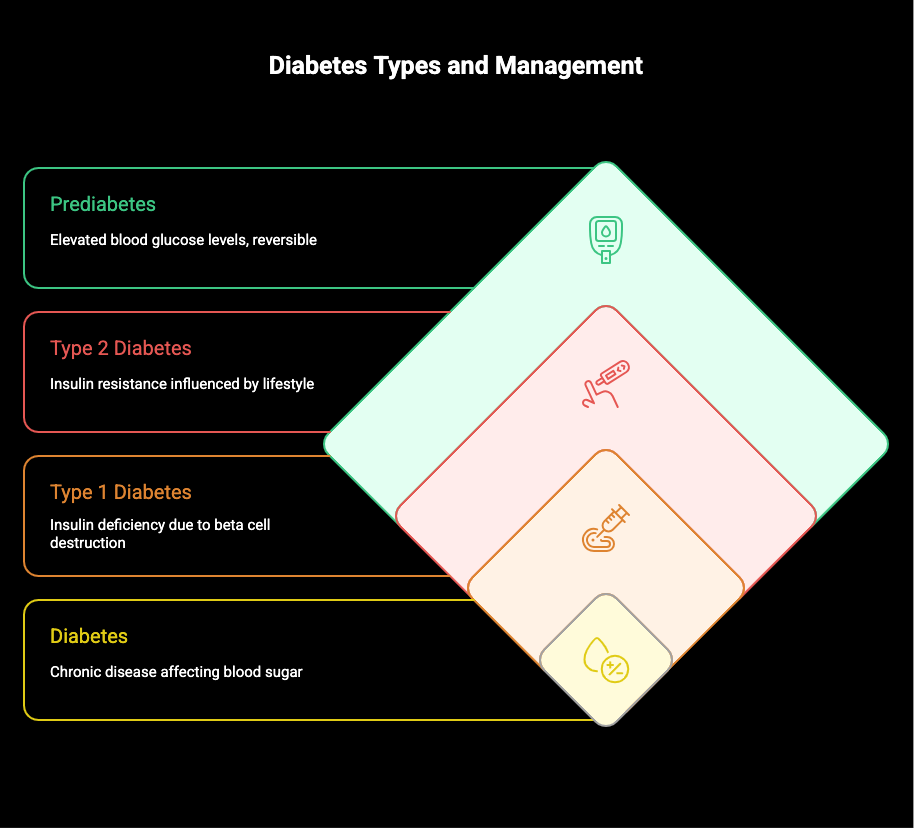
Distinguishing Between Type 1, Type 2, and Prediabetes
Understanding the distinctions among Type 1, Type 2, and prediabetes is essential for effective management. Type 1 is often diagnosed in childhood, where the body fails to produce enough insulin due to autoimmune factors. Type 2, prevalent in adults, is primarily linked to insulin resistance, often exacerbated by excess weight and lifestyle choices. Prediabetes, meanwhile, signals elevated blood glucose levels, typically indicating a higher risk of developing Type 2. Recognizing these differences helps tailor health strategies to improve overall wellness and management.
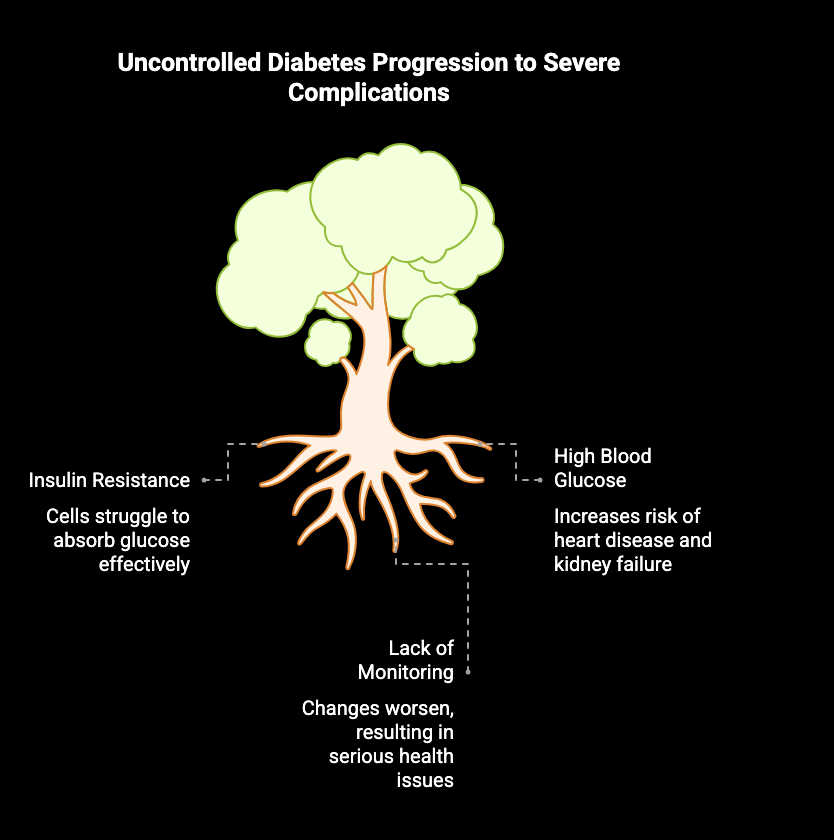
How Diabetes Progresses in the Body
Over time, diabetes can alter the way the body manages blood glucose levels, leading to complications. For instance, insulin resistance often develops, making it harder for insulin to help cells absorb glucose effectively. High blood glucose levels can trigger a host of problems, including increased risk of heart disease and kidney failure. If left unchecked, these changes may gradually worsen, resulting in serious health issues. Consistent monitoring and lifestyle changes can help manage these risks and promote better overall health.
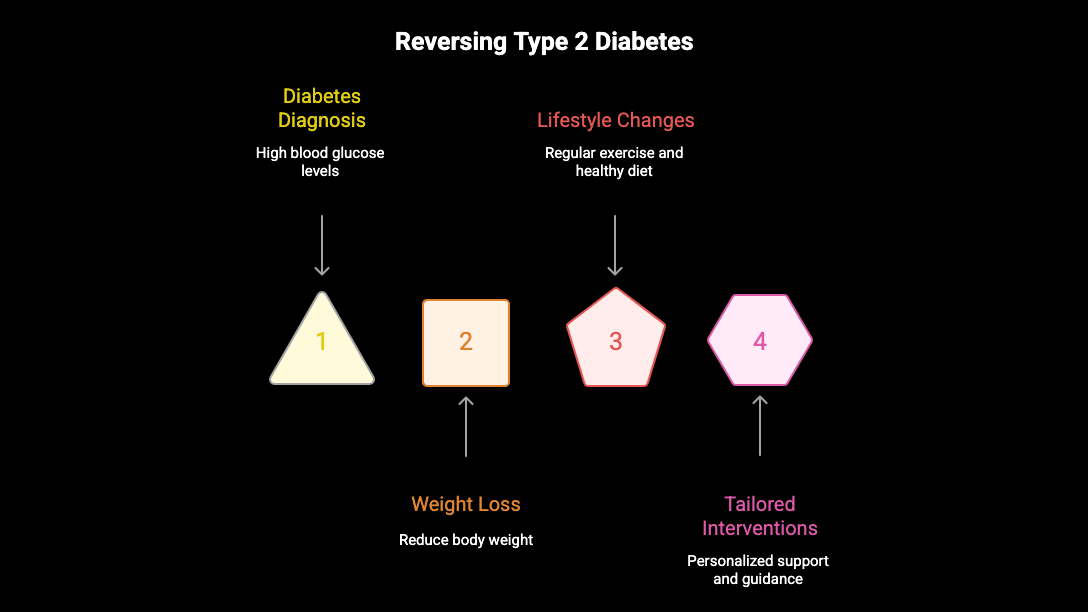
The Concept of Diabetes Reversal
Reversal of diabetes represents a hopeful shift in managing the condition, particularly for Type 2 diabetes. In this context, it refers to achieving normal glucose levels without the need for diabetes medications. This change often follows significant lifestyle modifications, including weight loss and increased physical activity, which enhance insulin sensitivity. Understanding this concept is crucial, as achieving remission can dramatically improve the quality of life and reduce the risk of complications associated with this chronic disease.
What Does “Reversal” Mean in Medical Terms?
In medical terms, “reversal” refers to the process of returning a disease to a state where it is no longer detectable or symptomatic. This can include significant improvement in blood sugar levels and other health markers, particularly in the context of diabetes management.
Remission Versus Complete Cure: What’s the Difference?
Remission refers to a period where diabetes symptoms are absent or significantly reduced, while a complete cure implies the permanent elimination of the disease. Understanding this distinction is crucial for managing diabetes effectively and setting realistic health goals.
Evidence on Reversing Type 2 Diabetes
Recent studies highlight promising evidence suggesting that reversing Type 2 diabetes is achievable for many individuals. Significant weight loss and lifestyle changes can enhance insulin sensitivity and stabilize blood glucose levels over time. Research, including clinical trials, shows that participants achieving remission of diabetes often maintained healthy body weight and engaged in regular physical activity. The American Diabetes Association emphasizes the importance of tailored interventions, demonstrating that with the right support, it’s possible to improve both health outcomes and quality of life.
Key Studies and Breakthrough Research
Recent studies have shed light on the potential for reversing Type 2 diabetes, revealing promising results in clinical trials. Research conducted by the American Diabetes Association indicates that significant weight loss and lifestyle changes lead to improved insulin sensitivity and blood glucose control. Notable trials, such as those from the University of Glasgow, highlight how participants achieved remission of diabetes symptoms through structured programs, suggesting a hopeful pathway for many facing this chronic disease. These findings encourage ongoing exploration and awareness in diabetes management.
How Common Is Type 2 Diabetes Reversal?
Type 2 diabetes reversal is increasingly recognized, with studies indicating that a significant number of individuals can achieve remission through lifestyle changes and medical interventions. However, prevalence varies based on factors like age, duration of diabetes, and adherence to treatment plans.
Medications That Support Remission
Several medications can play a supportive role in achieving remission from type 2 diabetes. For instance, drugs that enhance insulin sensitivity can help regulate blood glucose levels more effectively. Additionally, certain GLP-1 receptor agonists promote weight loss while controlling hunger, which is crucial for improving overall health. The American Diabetes Association also notes that SGLT2 inhibitors can reduce the risk of heart disease and kidney complications. Collaborating with a primary care provider ensures that the best medication plan is tailored to individual needs.
Current Research and Potential Future Therapies
Recent studies are shedding light on innovative therapies aimed at reversing diabetes. Research by the American Diabetes Association highlights a focus on enhancing beta cell function and optimizing insulin sensitivity through lifestyle interventions and medications. Emerging clinical trials are exploring the efficacy of very low-calorie diets and advanced bariatric surgery techniques, such as gastric bypass, to achieve significant weight loss and improve blood glucose levels. These developments offer hope for individuals striving for remission and a healthier future.
Conclusion
The journey through understanding diabetes has revealed that while complete reversal may not be possible for everyone, many individuals do achieve significant improvements. Embracing lifestyle changes like regular physical activity, weight management, and dietary adjustments can profoundly impact blood sugar levels and overall health. Continued research and emerging medical approaches offer hope for numerous individuals facing diabetes. Ultimately, collaborating with a healthcare provider can lead to personalized strategies that enhance both quality of life and the potential for diabetes remission.
Frequently Asked Questions
How long does it take to reverse type 2 diabetes with lifestyle changes?
Reversing Type 2 diabetes through lifestyle changes typically takes several months to years, depending on individual factors like age, weight loss, adherence to diet and exercise, and overall health. Consistency is key for achieving noticeable improvements in blood sugar levels.
Are there risks associated with reversing diabetes too quickly?
Reversing diabetes too quickly can lead to complications such as hypoglycemia, nutrient deficiencies, and metabolic disturbances. Rapid weight loss or drastic lifestyle changes may also cause emotional stress. It’s crucial to approach reversal gradually under medical supervision for safety and effectiveness.
Can weight loss alone reverse type 2 diabetes?
Weight loss can significantly improve insulin sensitivity and glycemic control, leading to remission of type 2 diabetes. However, it’s essential to combine weight loss with dietary changes and physical activity for optimal results, as individual responses vary. Consultation with a healthcare professional is recommended.