
Key Highlights
- The carbohydrates in the food you eat break down into glucose. This is the main source of energy for your body. The glucose moves in your blood as blood sugar.
- Insulin is a hormone that helps move glucose from your blood into your cells so you get energy.
- With diabetes, your carbohydrate metabolism does not work as it should. This can happen because of issues in making insulin or because your body does not use insulin well, which is called insulin resistance.
- When this happens, your glucose level stays high in the blood. A high glucose level for a long time can lead to health problems.
- The diabetes association with carbohydrates means it is important to manage how much of them you eat. This helps you control your blood sugar.
Introduction
Welcome to your guide on how carbohydrates move in the body, especially if you have diabetes. Managing diabetes mellitus can feel tough, and a big part of that is knowing how your food can change your blood sugar. Different types of diabetes change the way the body uses food for energy. This text will show you how carbohydrates become sugar, and how that can matter for your health.
How the Body Converts Carbohydrates to Glucose
Your body turns carbohydrates into glucose by using enzymes. These proteins in the digestive system help break down carbs into smaller pieces. After that, your body gets the simple glucose it can use. This whole process takes place in the digestive system.
As food leaves your stomach and enters your small intestine, the body releases more enzymes. These enzymes help break down different kinds of carbs. This includes starch found in a potato and sugar in fruit. They all turn into glucose in the end. The amount of glucose you get depends on the type and amount of carbs you eat.
This glucose comes from the breakdown of carbs in your food. It is ready to move into your blood, which will increase your glucose level and give you energy. If you are managing diabetes, it is very important to watch the amount of glucose that goes into your blood at one time. This helps stop your blood sugar from getting too high.
Differences in Digestion for People With Diabetes
The digestive system works the same, from person to person. But when you have diabetes mellitus, what happens after you eat can be different. Carbohydrates break down in the body the same way, and everyone gets glucose from them. The issue is with how the body reacts to that glucose. It’s not about how food gets broken down, but about the hormones that come into play afterwards.
After glucose moves into the bloodstream, someone who does not have diabetes will have a quick insulin secretion. This helps keep the blood glucose and blood sugar level steady. In people with diabetes, this insulin response may not happen, or it may not be enough, or it may not work well. So, the blood glucose and blood sugar stay high in the body. This problem is called high blood sugar or hyperglycemia because the glucose is left in the blood.
Your digestive system works to break down a piece of cake just like it would for anyone else. But, the effect on your body is more noticeable. Knowing this is key to see why you need to watch how many carbohydrates you eat. This is important for your health and to stop problems from happening later on.
Blood Sugar Regulation and Insulin’s Role
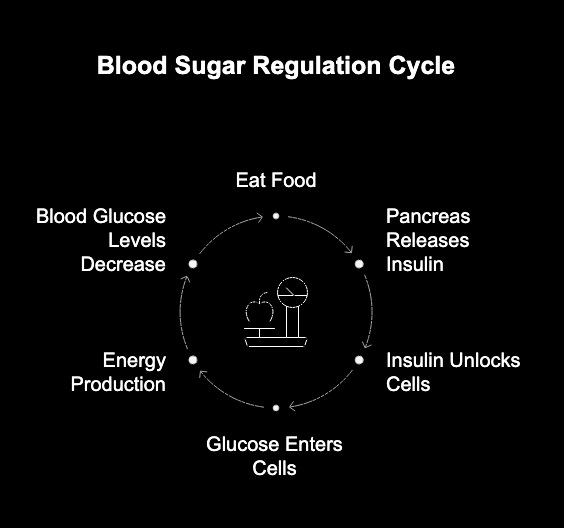
Your body has a smart way to control blood sugar. The main part of this system is a hormone called insulin. When you eat, this raises the level of blood glucose. After this, the pancreas steps in and releases insulin. Insulin works like a key. It unlocks your cells so glucose can get in and be used for energy.
In diabetes, this process does not work right. With insulin resistance, the locks on your cells act like they are “rusty,” so the key does not work well. In some cases, there is not enough insulin made from the start. This means there is too much glucose in the blood. This shows how important insulin’s role is in dealing with carbohydrates.
- It lowers your chance of getting heart disease.
- Even short breaks for activity during the day can help.
Stress and Blood Sugar Fluctuations
Stress, both in the body or in your mind, can have a big effect on your blood sugar. When you feel stress, your body makes more hormones like cortisol and adrenaline. These are known as “fight or flight” hormones. They make your liver send more sugar into your blood, so you get fast energy.
If you do not have diabetes, your body will release more insulin to deal with a spike in blood sugar. But if you have diabetes, you might not have enough insulin. This can cause higher levels of blood sugar. Chronic stress can also push up your blood pressure. It can make it harder to stick to your diabetes plan.
Finding healthy ways to manage stress is vital:
- Try things like deep breathing or meditation to help you relax.
- Be active by doing regular physical activity.
- Make sure you have enough good sleep.
- Stay in touch with friends, family, or a support group.
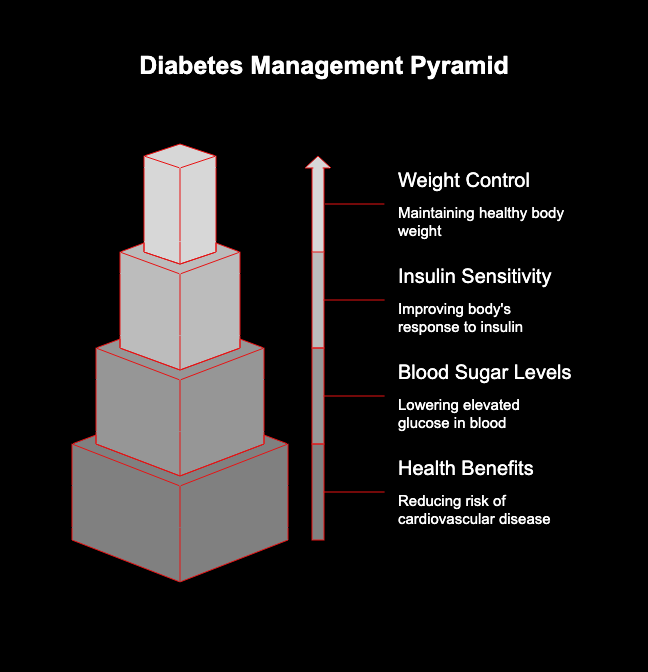
Weight Management and Its Effects on Blood Sugar
Keeping your body weight under control is very important for managing diabetes, mainly type 2 diabetes. Having too much body fat, especially around your stomach, makes insulin resistance worse. This means your body cannot use insulin in a good way. Because of this, your blood sugar level can go up.
Losing a small amount of body weight, just 5-10% of what you start with, can be good for your health. It can help make your insulin sensitivity better. It also helps lower your blood sugar levels. Because of this, you may cut down the risk of getting cardiovascular disease and other problems linked to diabetes.
Here are some key aspects of weight management:
- Try to eat a balanced diet that has lots of whole foods.
- Use portion control, so you can manage the calories you eat.
- Make time for regular physical activity in your daily routine.
- Weight loss may help lower both your blood pressure and your cholesterol.
- You should work with your healthcare team to find weight goals that are realistic and that you can achieve.
Conclusion
Knowing how carbohydrates and diabetes are linked is important for managing diabetes in the best way. The type of carbohydrate you eat can change your blood sugar. If you understand how the glycemic index works and practice good portion control, you will help keep your blood sugar stable. You should pick healthy carbs and add physical activity and good sleep habits to your routine. These are important steps to take for better blood sugar. If you want to learn more about your carbohydrates or feel ready to start working on your health, you can get a free consultation with our experts. Take the first step and start taking charge of your health now!
Frequently Asked Questions
Why do different carbohydrates affect blood sugar differently in diabetes?
Different kinds of carbs can change blood sugar in different ways. This is because of the way they are made and their glycemic index. Simple sugars are broken down fast. This makes your blood glucose level go up quickly. Complex carbohydrates have fiber. This slows down how fast they are digested. So, your blood sugar rises slowly. This is why the diabetes association says complex carbohydrates are better if you want to keep a steady blood glucose level.
How can people with diabetes manage carbohydrate intake to control blood sugar?
As part of diabetes treatment, you need to watch how many carbs you eat. You can do this with carb counting and portion control. Glucose meters help you check your body’s reaction to food. This way, you can change what you do to get the best result. The goal is to balance the primary source of energy, which is carbs, with your medicine and how much you move. This helps keep your blood sugar steady.
Which foods with carbohydrates are best for people living with diabetes?
The best foods for people who want to manage their blood sugar have a good diabetes association. Pick nutrient-dense foods like whole grains. Some good examples are oats and brown rice. You can also go for legumes, non-starchy vegetables, and fruits like berries. These foods are packed with fiber. Fiber helps to slow down how fast your body takes in sugar. This makes it easier to keep your blood sugar at a good level. Try to eat these foods often, instead of starchy vegetables.
Practical Tips for Managing Carbohydrates With Diabetes
For better diabetes treatment, try to spread out your carbs during the whole day. It is good to eat carbs together with some protein and fat. Make time for physical activity, and check your blood sugar to stay in a healthy range. Choose foods that have more fiber and are made from whole ingredients. This can help keep your blood sugar in control and be better for your health.


