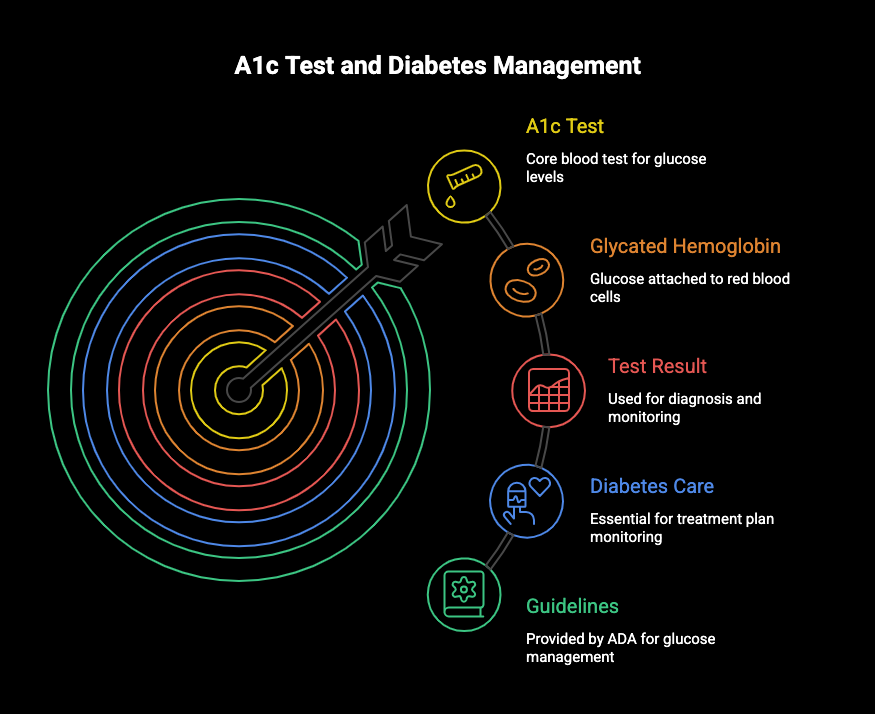
Key Highlights
Here are the key takeaways about the A1c test:
- The A1c is a crucial blood test that measures your average blood sugar over the past two to three months.
- It works by measuring the percentage of glycated hemoglobin, which is glucose attached to your red blood cells.
- Healthcare providers use the test result to diagnose prediabetes and Type 2 diabetes.
- It is an essential part of diabetes care for monitoring how well a treatment plan is working.
- The American Diabetes Association provides guidelines for target A1c levels to manage blood glucose effectively.
Introduction
Have you ever wondered what an A1c test reveals about your health? It’s a simple blood test that provides a broader view than a daily finger prick test. Instead of measuring your blood glucose level at a single moment, the A1c test calculates your average blood sugar over the past two to three months. This is done by checking the percentage of your red blood cells that have glucose molecules attached to them, giving you and your provider a valuable long-term perspective on your body’s glucose management.
Have you ever pondered what it truly means when a healthcare professional mentions your A1C levels? Imagine if one number could unveil your sugar story over an extended period. This is precisely what Hemoglobin A1C does, offering a comprehensive snapshot that stretches back three months, similar to a time-lapse on your smartphone.
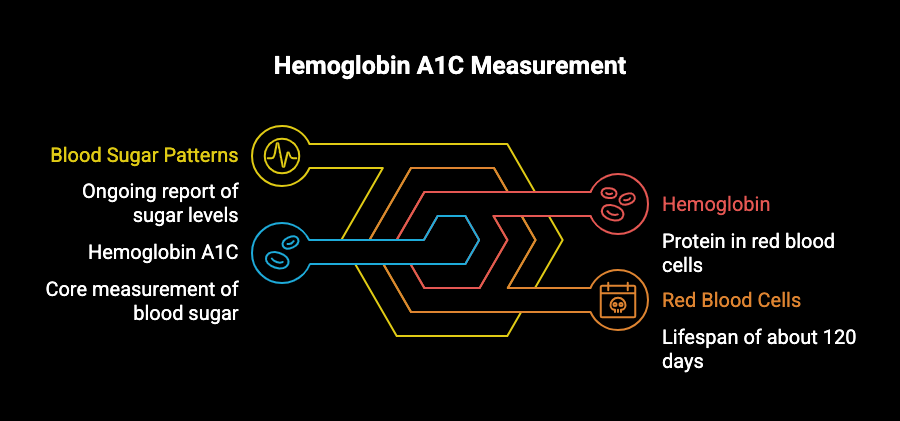
What is Hemoglobin A1C?
Hemoglobin A1C is more than just a medical term; it’s a crucial blood test. This test measures the amount of sugar adhered to your hemoglobin, which is a protein in your red blood cells. Since these cells have a lifespan of about 120 days, your A1C levels provide an ongoing report of your blood sugar patterns over significant timeframes. Think of it as a caramel crust forming gradually with every sugary intake.
Understanding Your A1C Levels
The principle is straightforward: the more sugar circulating in your blood, the higher your A1C levels will be. This understanding is vital because even if your day-to-day blood sugars appear normal, unseen spikes after meals can elevate your A1C. Hence, even occasional indulgences can reflect in your overall A1C count.
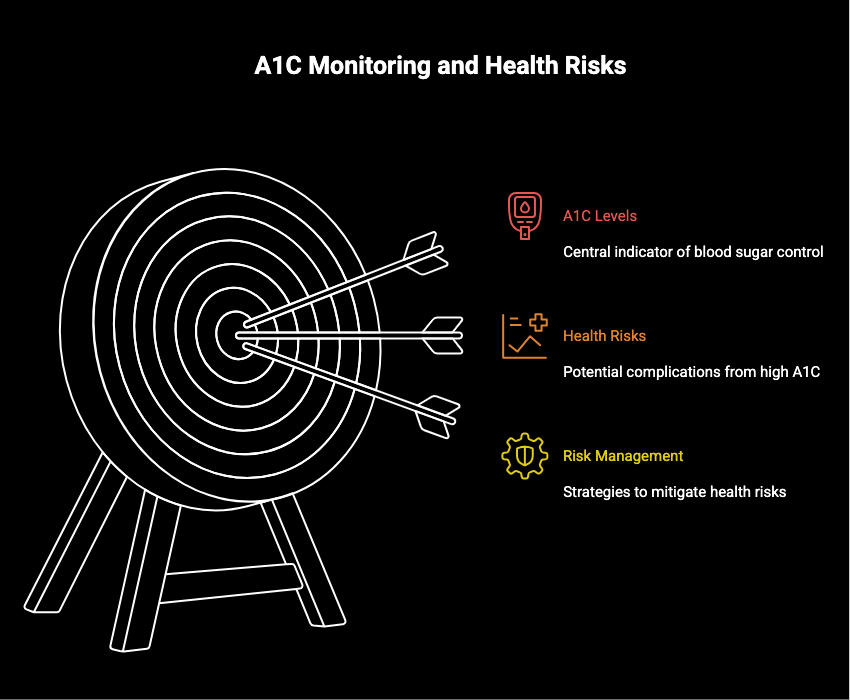
The Importance of Monitoring A1C
Why does this number matter? Elevated A1C levels correlate with greater risk factors for complications such as eye, kidney, and nerve damage. Therefore, monitoring these levels becomes a vital component in managing and mitigating these risks.
https://www.nhlbi.nih.gov/health-topics/iron-deficiency-anemia
Conclusion
To gain further insight into how blood sugar interacts with your body and affects your A1C, check out the video linked in the description. By familiarizing yourself with the intricacies of this simple yet telling number, you can better navigate the path to optimal health. Generally, it is recommended to get your A1c checked at least twice a year if your levels are stable and within target. If your treatment has changed or your levels are not under control, your healthcare provider may suggest testing quarterly.
And don’t forget, if you found this information helpful, subscribe to our channel, Con md, to stay updated with more health insights!


