
Key Highlights
Here are the main points to remember about your A1C:
- The A1C test is a simple blood test. It shows what your average blood sugar levels have been for the last three months.
- A health care provider uses this test for diabetes diagnosis. It also helps them check if your plan to control blood sugar is working.
- A1C results show your blood sugar over time. Daily checks only tell you what it is right now.
- When you keep your A1C in a good range, you can lower your risk of diabetes complications.
- Lifestyle changes in your diet and exercise habits can help drop your A1C and improve your blood sugar levels.
Introduction
If you have diabetes mellitus, you may hear your health care provider talk about the A1C test. But you might ask, what does the A1C number really mean? The A1C test is very important, because it gives you a bigger look at how your blood sugar has been over several months. It is not just any number. A1C helps show your overall health and gives advice for you and your health care team. You can use this number to help feel your best. In this guide, you will read all about this key test and find out what you need to know for your health.
How the A1C Test Measures Blood Sugar
Have you ever thought about how one blood test can tell so much about your blood sugar history? The answer is in your red blood cells and a protein they have called hemoglobin. When blood sugar moves around in your blood, it glues itself to the hemoglobin molecules in the blood cells. This thing that happens is called glycation.
When you have more sugar in your blood, more of it sticks to the hemoglobin. Your red blood cells stay in the body for around three months. The A1C test shows how much of your hemoglobin has sugar attached to it. This test gives a long-term view and shows a percentage. It can also tell you the estimated average glucose or the average glucose level. Your blood cells, mainly red blood cells, help in this process.
This A1C test is not like a daily blood sugar check. A daily check gives you your glucose number at that one time. A1C, on the other hand, tells you your average blood sugar levels over a longer period. This bigger picture is very important. It helps you see how you are managing diabetes, and what it means for your health over time.
Differences Between A1C and Daily Glucose Testing
It’s common for people to mix up the A1C test with the blood glucose tests you do every day at home. Both check the sugar level in the blood, but they tell you different things. A blood glucose test done by finger prick each day shows how much sugar is in your blood right at that moment.
This feedback you get right away is good for making everyday choices. For example, it can help you change your insulin or pick what food to eat. The A1C test is different. It does not show you the daily changes in your sugar levels. A1C tells you your average glucose from the last three months.
Here’s a simple breakdown:
- Daily Glucose Test (Finger Prick): This shows your blood sugar level at that moment. You get the number right away.
- A1C Test: This shows how your blood sugar has been for the past two or three months. It helps you see your overall blood sugar control.
Both tests are key. Daily checks help you and your health care team handle things right now. The A1C test gives the big-picture view. It helps your health care team see how well your plan is working over time.
Long-Term vs Short-Term Blood Sugar Control
Knowing how short-term and long-term blood sugar control works is important for people who want to manage diabetes well. When you check your daily glucose, you see your blood sugar levels right then. Your blood sugar can go up or down. It may change because of what you ate, your physical activity, or if you feel stress. This daily check shows a short-term look at your blood sugar levels.
The A1C test is different because it gives a look at your blood sugar over a long period. It checks the amount of glucose that sticks to red blood cells. These blood cells live in your body for about three months. So, the A1C test gives an average of your blood sugar levels during that time. This way, it does not just show ups and downs in one day. It lets you see the whole picture of your blood sugar and trends over several months.
This table highlights the key differences:
|
Feature |
Daily Glucose Test |
A1C Test |
|---|---|---|
|
Timeframe |
Measures blood sugar at a single moment. |
Reflects average blood sugar over 2-3 months. |
|
Purpose |
Guides immediate decisions (food, insulin). |
Assesses long-term management and risk. |
|
Measurement |
Reports a specific number (e.g., 150 mg/dL). |
Reports a percentage (e.g., 7.0%). |
An A1C test does not show if you get a quick rise or fall in blood sugar. It does help find out if your blood sugar has been high for the past few months. This makes it a good way to check long-term blood sugar control.
Understanding Thresholds and Diagnostic Criteria
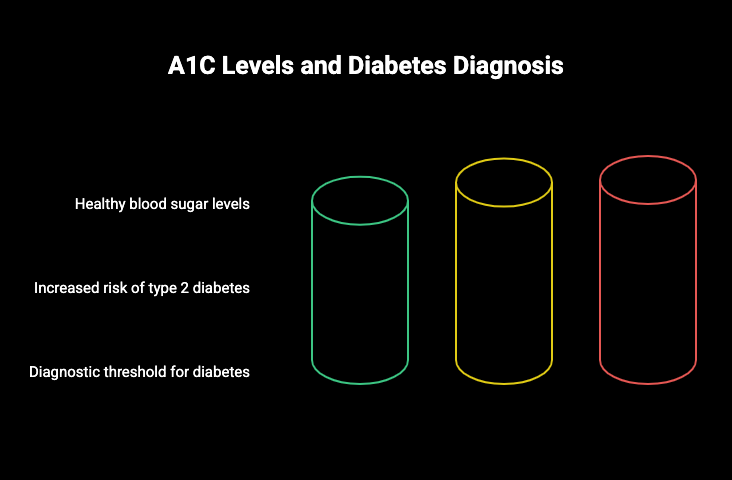
For the diagnosis of diabetes, health care workers use A1C thresholds set by groups such as the American Diabetes Association. A1C percentages show what your blood sugar levels look like on average. These numbers help tell if you are in a normal range, if you have prediabetes, or if your blood sugar is high enough for a diabetes diagnosis.
Knowing about these numbers can help you get what your results mean for your health. If your A1C is below 5.7%, that is normal. A result from 5.7% to 6.4% shows prediabetes. This means you are more at risk for type 2 diabetes. A diagnosis of diabetes usually is made when A1C is 6.5% or higher.
Here are the diagnostic criteria at a glance:
|
Diagnosis |
A1C Level |
|---|---|
|
Normal |
Below 5.7% |
|
Prediabetes |
5.7% to 6.4% |
|
Diabetes |
6.5% or above |
When you first get checked for type 2 diabetes, the starting point is a level of 6.5%. Most people with this condition aim to keep their levels below 7%. If your test shows you have diabetes, your doctor will do another test to be sure.
Conclusion
Knowing your A1C levels is very important for good diabetes care. This test shows you your average blood sugar levels from the last few months. It helps you and your doctor make better choices for your health. When you watch your A1C, you get to understand more about how your blood sugar goes up and down. This helps you feel better and manage your health in the right way. What you eat and how much you move your body can change your A1C, so making smart choices every day matters a lot. If you feel unsure or want some help with your A1C or blood sugar levels, you can always ask for a free consultation. You are not alone. There is support ready for you so you can feel good about your health journey.
Frequently Asked Questions
How often should I get my A1C level checked?
Experts say you should get an A1C test at least two times a year if you are meeting your treatment goals. The health care provider may want you to have this test more often, maybe every three months. This can happen if your treatment plan changes, or if your blood sugar is not well-managed for better disease control.
Can lifestyle changes really make a big difference in my A1C?
Yes, you can lower your A1C by choosing a healthy lifestyle. Simple steps, like changing what you eat and moving your body more often, can help bring down blood sugar levels. Losing even a small amount of weight is good, too. These changes can help your blood sugar as much as, or even more than, some diabetes medications. A healthy lifestyle is important for managing blood sugar over the long run.
Does the A1C test show recent changes in blood sugar?
No, the A1C test does not show if you have had quick or recent changes in your blood sugar. It tells you your estimated average glucose to give you an idea of your blood glucose over the last three months. If you want to know your blood sugar at this moment, you should use a daily glucose meter. The meter will give you quick results from a blood sugar test, so you can see your average glucose right now.


